Tập tin:Tide.Bridgeport.50h.svg

Kích thước bản xem trước PNG này của tập tin SVG: 717×437 điểm ảnh. Độ phân giải khác: 320×195 điểm ảnh | 640×390 điểm ảnh | 1.024×624 điểm ảnh | 1.280×780 điểm ảnh | 2.560×1.560 điểm ảnh.
Tập tin gốc (tập tin SVG, 717×437 điểm ảnh trên danh nghĩa, kích thước: 42 kB)
Tập tin này từ Wikimedia Commons. Trang miêu tả nó ở đấy được sao chép dưới đây. Commons là kho lưu trữ tập tin phương tiện có giấy phép tự do. Bạn có thể tham gia. |
Miêu tả
| Miêu tảTide.Bridgeport.50h.svg |
English: Fifty hours of tide heights at Bridgeport, Connecticut, U.S.A. as calculated from the Harmonic Constituent data aligned with 0h Sunday 1st September 1991. Calculations and plotting done by a MatLab script (found here), devised by NickyMcLean as part of some investigations for the New Zealand Electricity Commission and given as an example in the article on Arthur Thomas Doodson. SVG version of File:Tide.Bridgeport.50h.png. |
| Ngày | |
| Nguồn gốc | Tác phẩm được tạo bởi người tải lên |
| Tác giả | Cody Logan (clpo13) |
| SVG genesis InfoField | This W3C-invalid diagram was created with MATLAB. |
| Mã nguồn InfoField | MATLAB code% Speed in degrees per hour for various Earth-Moon-Sun astronomical attributes, as given in Tides, Surges and Mean Sea-Level, D.T. Pugh.
clear EMS;
% T + s - h +15 w0: Nominal day, ignoring the variation followed via the Equation of Time.
EMS.T = +360/(1.0350)/24; %+14.492054485 w1: is the advance of the moon's longitude, referenced to the Earth's zero longitude, one full rotation in 1.0350 mean solar days.
EMS.s = +360/(27.3217)/24; % +0.5490141536 w2: Moon around the earth in 27.3217 mean solar days.
EMS.h = +360/(365.2422)/24; % +0.0410686388 w3: Earth orbits the sun in a tropical year of 365.24219879 days, not the 365.2425 in 365 + y/4 - y/100 + y/400. Nor with - y/4000.
EMS.p = +360/(365.25* 8.85)/24; % +0.0046404 w4: Precession of the moon's perigee, once in 8.85 Julian years: apsides.
EMS.N = -360/(365.25*18.61)/24; % -0.00220676 w5: Precession of the plane of the moon's orbit, once in 18.61 Julian years: negative, so recession.
EMS.pp= +360/(365.25*20942)/24; % +0.000001961 w6: Precession of the perihelion, once in 20942 Julian years.
% T + s = 15.041068639°/h is the rotation of the earth with respect to the fixed stars, as both are in the same sense.
% Reference Angular Speed Degrees/hour Period in Days. Astronomical Values.
% Sidereal day Distant star ws = w0 + w3 = w1 + w2 15.041 0.9973
% Mean solar day Solar transit of meridian w0 = w1 + w2 - w3 15 1
% Mean lunar day Lunar transit of meridian w1 14.4921 1.0350
% Month Draconic Lunar ascending node w2 + w5 .5468 27.4320
% Month Sidereal Distant star w2 .5490 27.3217 27d07h43m11.6s 27.32166204
% Month Anomalistic Lunar Perigee (apsides) w2 - w4 .5444 27.5546
% Month Synodic Lunar phase w2 - w3 = w0 - w1 .5079 29.5307 29d12h44m02.8s 29.53058796
% Year Tropical Solar ascending node w3 .0410686 365.2422 365d05h48m45s 365.24218967 at 2000AD. 365.24219879 at 1900AD.
% Year Sidereal Distant star .0410670 365.2564 365d06h09m09s 365.256363051 at 2000AD.
% Year Anomalistic Solar perigee (apsides) w3 - w6 .0410667 365.2596 365d06h13m52s 365.259635864 at 2000AD.
% Year nominal Calendar 365 or 366
% Year Julian 365.25
% Year Gregorian 365.2425
% Obtaining definite values is tricky: years of 365, 365.25, 365.2425 or what days? These parameters also change with time.
clear Tide;
% w1 w2 w3 w4 w5 w6
Tide.Name{1} = 'M2'; Tide.Doodson{ 1} = [+2 0 0 0 0 0]; Tide.Title{ 1} = 'Principal lunar, semidiurnal';
Tide.Name{2} = 'S2'; Tide.Doodson{ 2} = [+2 +2 -2 0 0 0]; Tide.Title{ 2} = 'Principal solar, semidiurnal';
Tide.Name{3} = 'N2'; Tide.Doodson{ 3} = [+2 -1 0 +1 0 0]; Tide.Title{ 3} = 'Principal lunar elliptic, semidiurnal';
Tide.Name{4} = 'L2'; Tide.Doodson{ 4} = [+2 +1 0 -1 0 0]; Tide.Title{ 4} = 'Lunar semi-diurnal: with N2 for varying speed around the ellipse';
Tide.Name{5} = 'K2'; Tide.Doodson{ 5} = [+2 +2 -1 0 0 0]; Tide.Title{ 5} = 'Sun-Moon angle, semidiurnal';
Tide.Name{6} = 'K1'; Tide.Doodson{ 6} = [+1 +1 0 0 0 0]; Tide.Title{ 6} = 'Sun-Moon angle, diurnal';
Tide.Name{7} = 'O1'; Tide.Doodson{ 7} = [+1 -1 0 0 0 0]; Tide.Title{ 7} = 'Principal lunar declinational';
Tide.Name{8} = 'Sa'; Tide.Doodson{ 8} = [ 0 0 +1 0 0 0]; Tide.Title{ 8} = 'Solar, annual';
Tide.Name{9} = 'nu2'; Tide.Doodson{ 9} = [+2 -1 +2 -1 0 0]; Tide.Title{ 9} = 'Lunar evectional constituent: pear-shapedness due to the sun';
Tide.Name{10} = 'Mm'; Tide.Doodson{10} = [ 0 +1 0 -1 0 0]; Tide.Title{10} = 'Lunar evectional constituent: pear-shapedness due to the sun';
Tide.Name{11} = 'P1'; Tide.Doodson{11} = [+1 +1 -2 0 0 0]; Tide.Title{11} = 'Principal solar declination';
Tide.Constituents = 11;
% Because w0 + w3 = w1 + w2, the basis set {w0,...,w6} is not independent. Usage of w0 (or of EMS.T) can be eliminated.
% For further pleasure w2 - w6 correspond to other's usage of w1 - w5.
% Collect the basic angular speeds into an array as per A. T. Doodson's organisation. The classic Greek letter omega is represented as w.
clear w;
% w(0) = EMS.T + EMS.s - EMS.h; % This should be w(0), but MATLAB doesn't allow this!
w(1) = EMS.T;
w(2) = EMS.s;
w(3) = EMS.h;
w(4) = EMS.p;
w(5) = EMS.N;
w(6) = EMS.pp;
% Prepare the basis frequencies, of sums and differences. Doodson's published coefficients typically have 5 added
% so that no negative signs will disrupt the layout: the scheme here does not have the offset.
disp('Name °/hour Hours Days');
for i = 1:Tide.Constituents
Tide.Speed(i) = sum(Tide.Doodson{i}.*w); % Sum terms such as DoodsonNumber(j)*w(j) for j = 1:6.
disp([int2str(i),' ',Tide.Name{i},' ',num2str(Tide.Speed(i)),' ',num2str(360/Tide.Speed(i)),' ',num2str(15/Tide.Speed(i)),' ',Tide.Title{i}]);
end
clear Place;
% The amplitude H and phase for each constituent are determined from the tidal record by least-squares
% fitting to the observations of the amplitudes of the astronomical terms with expected frequencies and phases.
% The number of constituents needed for accurate prediction varies from place to place.
% In making up the tide tables for Long Island Sound, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
% uses 23 constituents. The eleven whose amplitude is greater than .1 foot are:
Place(1).Name = 'Bridgeport, CT'; % Counting time in hours from midnight starting Sunday 1 September 1991.
% M2 S2 N2 L2 K2 K1 O1 Sa nu2 Mm P1...
Place(1).A = [ 3.185 0.538 0.696 0.277 0.144 0.295 0.212 0.192 0.159 0.108 0.102]; % Tidal heights (feet)
Place(1).P = [-127.24 -343.66 263.60 -4.72 -2.55 142.02 505.93 301.5 45.70 86.82 340.11]; % Phase (degrees).
% The values for these coefficients are taken from http://www.math.sunysb.edu/~tony/tides/harmonic.html
% which originally came from a table published by the US. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
% Calculate a tidal height curve, in terms of hours since the start time.
PlaceCount = 1;
Colour=cellstr(char('b','r','g','c','m','y','k')); % A collection.
clear y;
step = 0.125; LastHour = 720; % 8760 hours in a year.
n = LastHour/step + 1;
y(1:n,1:PlaceCount) = 0;
t = (0:step:LastHour);
for it = 1:PlaceCount
i = 0;
for h = 0:step:LastHour
i = i + 1;
y(i,it) = sum(Place(it).A.*cosd(Tide.Speed*h + Place(it).P)); %Sum terms A(j)*cos(speed(j)*h + p(j)) for j = 1:Tide.Constituents.
end % Should use cos(ix) = 2*cos([i - 1]*x)*cos(x) - cos([i - 2]*x), but, for clarity...
end
figure('Position', [100, 100, 850, 400]); clf; hold on;
title('Tidal Height, Bridgeport, CT');
xlabel('Hours since 0h Sunday 1st September 1991'); ylabel('Feet');
xlim([0 50]);
for it = 1:PlaceCount
plot(t,y(1:n,it),Colour{it});
end
%legend(Place(1:PlaceCount).Name,'Location','NorthWest');
|
Giấy phép
Tôi, người giữ bản quyền tác phẩm này, từ đây phát hành nó theo giấy phép sau:
| Tập tin này được phân phối theo Creative Commons Hiến tặng vào Phạm vi Công cộng Toàn thế giới CC0. | |
| Người nào gán tài liệu này với tác phẩm nghĩa là đã hiến tác phẩm cho phạm vi công cộng bằng cách từ bỏ mọi quyền lợi của người đó đối với tác phẩm theo quy định của luật bản quyền, có hiệu lực trên toàn thế giới và các quyền lợi pháp lý phụ mà người đó có được trong tác phẩm, đến mức độ mà luật pháp cho phép. Bạn được tự do sao chép, phân phối, và biểu diễn tác phẩm này, tất cả đều không bắt buộc ghi công.
http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/deed.enCC0Creative Commons Zero, Public Domain Dedicationfalsefalse |
Chú thích
Ghi một dòng giải thích những gì có trong tập tin này
Chart showing fifty hours of calculated tide heights at Bridgeport, Connecticut, starting September 1, 1991
Khoản mục được tả trong tập tin này
mô tả
Giá trị nào đó không có khoản mục Wikidata
5 4 2017
Lịch sử tập tin
Nhấn vào ngày/giờ để xem nội dung tập tin tại thời điểm đó.
| Ngày/giờ | Hình xem trước | Kích cỡ | Thành viên | Miêu tả | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hiện tại | 23:07, ngày 5 tháng 4 năm 2017 |  | 717×437 (42 kB) | Clpo13 | Reduce font size |
| 22:31, ngày 5 tháng 4 năm 2017 |  | 717×437 (42 kB) | Clpo13 | W3 valid | |
| 22:11, ngày 5 tháng 4 năm 2017 | 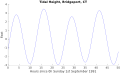 | 717×437 (42 kB) | Clpo13 | User created page with UploadWizard |
Trang sử dụng tập tin
Có 1 trang tại Wikipedia tiếng Việt có liên kết đến tập tin (không hiển thị trang ở các dự án khác):
Sử dụng tập tin toàn cục
Những wiki sau đang sử dụng tập tin này:
- Trang sử dụng tại en.wikipedia.org
Đặc tính hình
Tập tin này chứa thông tin bổ sung, có thể được thêm từ máy ảnh kỹ thuật số hoặc máy quét được sử dụng để tạo hoặc số hóa tệp.
Nếu tập tin đã được sửa đổi so với trạng thái ban đầu, một số chi tiết có thể không phản ánh đầy đủ tập tin đã sửa đổi.
| Chiều ngang | 717 |
|---|---|
| Chiều cao | 437 |